AQI Explained: What is Air Quality Index and why Indian cities turn hazardous every Diwali
What is AQI and how it works: Why do Diwali celebrations cause dangerous spikes in air pollution and how can you protect health?
ADVERTISEMENT
What Is AQI?
The Air Quality Index (AQI) is a standardized system used globally to measure and communicate air pollution levels. It assesses the concentration of pollutants such as particulate matter (PM2.5 and PM10), nitrogen dioxide (NO₂), sulfur dioxide (SO₂), carbon monoxide (CO), and ozone (O₃). In India, AQI values are categorized as follows:
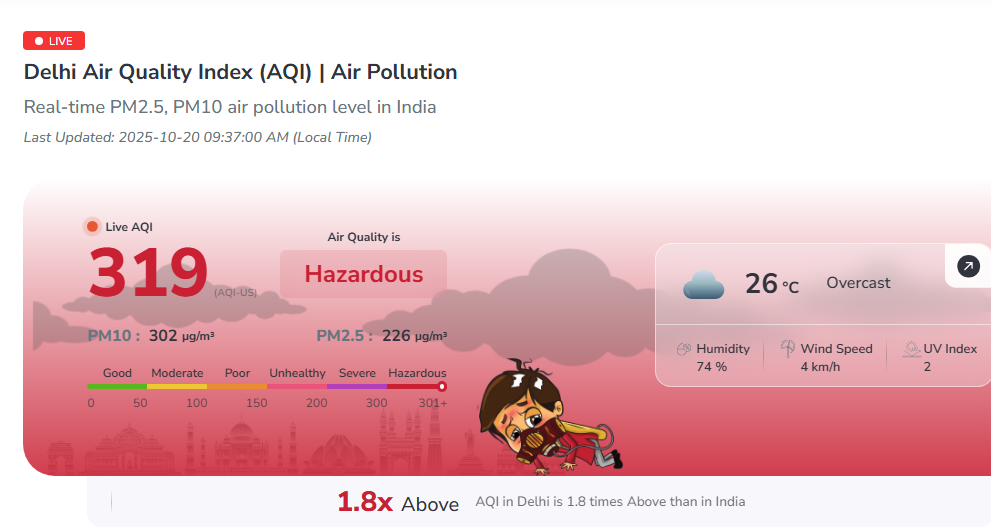
0–50: Good
51–100: Satisfactory
101–200: Moderate
201–300: Poor
301–400: Very Poor
401–500: Severe
An AQI above 300 is considered hazardous, posing significant health risks, especially to vulnerable groups like children, the elderly, and those with pre-existing respiratory conditions.
AQI in India: A Growing Concern
India faces a persistent air pollution challenge. In 2024, 94 of the 100 most polluted cities globally were in India, with New Delhi topping the list for the highest AQI levels
This situation worsens during the Diwali festival, when the use of firecrackers leads to a significant spike in pollution levels.
Diwali and Its Impact on AQI
Diwali, the festival of lights, is celebrated with enthusiasm across India. However, the widespread use of firecrackers during the festivities contributes to a sharp increase in air pollution. For instance, in Delhi, AQI levels have often crossed the 'very poor' category during Diwali, leading to health advisories and the implementation of emergency measures
Similar trends were observed in other cities like Ghaziabad, Noida, and Kolkata, where AQI levels deteriorated to 'very poor' and 'severe' categories during the festival.
Government Measures: Graded Response Action Plan (GRAP)
To combat the deteriorating air quality during Diwali, the government has implemented the Graded Response Action Plan (GRAP). This plan involves a series of escalating measures based on AQI levels:
Stage I: Ban on construction activities, use of diesel generators, and mechanized sweeping of roads.
Stage II: Enhanced restrictions, including closure of brick kilns and stone crushers, and stricter enforcement of pollution norms.
Stage III: Implementation of public health emergency measures, such as halting non-essential construction and industrial activities.
These measures aim to reduce pollution levels and mitigate health risks during high-pollution periods like Diwali.
Health Implications of Poor AQI
Exposure to poor air quality during Diwali can lead to various health issues:
Respiratory Problems: Increased risk of asthma, bronchitis, and other respiratory conditions.
Cardiovascular Issues: Elevated risk of heart attacks and strokes.
Eye Irritation: Burning sensations and watering of eyes.
Skin Problems: Rashes and irritation due to exposure to pollutants.
Vulnerable groups, including children, the elderly, and individuals with pre-existing health conditions, are particularly at risk.
Steps to Mitigate AQI Impact During Diwali
To minimize the adverse effects of Diwali on air quality and health:
Limit Firecracker Use: Opt for eco-friendly or virtual celebrations.
Stay Indoors: Remain indoors during peak pollution hours, typically post-sunset.
Use Air Purifiers: Utilize air purifiers with HEPA filters to reduce indoor pollution.
Wear Masks: Use N95 masks to protect against inhalation of fine particulate matter.
Monitor AQI Levels: Stay informed about real-time AQI levels through reliable sources.
Understanding AQI and its implications is crucial, especially during festivals like Diwali, when air pollution levels can reach hazardous levels. By adopting responsible practices and adhering to government guidelines, we can celebrate the festival safely while protecting our health and the environment.
Read more: Delhi’s air quality plummets to ‘Severe’ levels amid Diwali celebrations